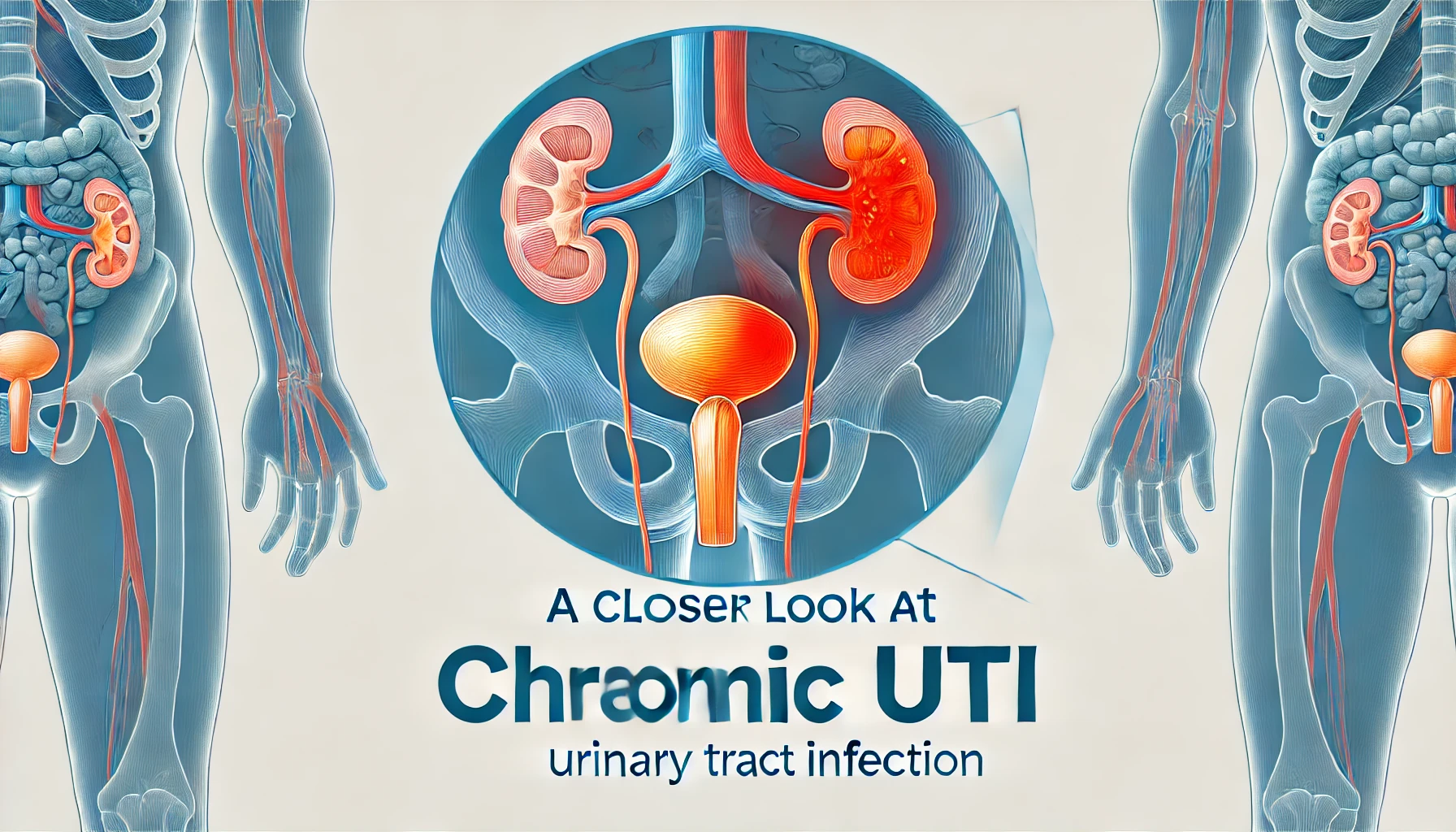
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are common bacterial infections that can affect any part of your urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. While UTIs are treatable, early recognition and proper treatment are crucial to prevent complications. At Raksha Hospital, our urology specialists provide comprehensive care for all types of urinary tract infections.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing infection and inflammation. The most common type is a bladder infection (cystitis), but UTIs can also affect the kidneys (pyelonephritis) and urethra (urethritis).
🫁 Bladder Infection (Cystitis)
The most common type of UTI, affecting the bladder. Usually caused by E. coli bacteria and more common in women.
🫀 Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
A more serious infection that can spread from the bladder to the kidneys. Requires immediate medical attention.
🚰 Urethra Infection (Urethritis)
Infection of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body.
Common UTI Symptoms
Recognizing UTI symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on which part of the urinary tract is affected:
🚨 Common Symptoms
- Frequent Urination: Feeling the need to urinate more often than usual
- Burning Sensation: Pain or burning when urinating
- Urgency: Strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Cloudy Urine: Urine appears cloudy or has a strong odor
- Blood in Urine: Pink, red, or cola-colored urine
⚠️ Severe Symptoms (Seek Immediate Care)
- High Fever: Temperature above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Back Pain: Pain in the lower back or side
- Nausea & Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Confusion: Mental changes, especially in elderly
- Chills: Shaking or chills with fever
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes UTIs and who is at risk helps in prevention:
🔬 Common Causes
- Bacterial Entry: Bacteria from the digestive tract entering the urethra
- E. coli Bacteria: Most common cause, accounting for 80-90% of UTIs
- Sexual Activity: Can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract
- Catheter Use: Medical devices can introduce bacteria
- Blocked Urine Flow: Kidney stones or enlarged prostate
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Gender: Women are more prone due to shorter urethra
- Age: Elderly individuals have higher risk
- Diabetes: High blood sugar promotes bacterial growth
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes affect urinary tract
- Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Structural issues from birth
Diagnosis of UTIs
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Our urology specialists use various diagnostic methods:
🔬 Urine Analysis
- Examination of urine for white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria
- Dipstick test for nitrites and leukocyte esterase
- Microscopic examination of urine sediment
🧪 Urine Culture
- Growing bacteria from urine sample to identify specific organisms
- Determining which antibiotics are most effective
- Helping guide treatment decisions
📷 Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound to check for kidney stones or blockages
- CT scan for detailed urinary tract imaging
- X-rays for structural abnormalities
🔍 Cystoscopy
- Direct visualization of bladder and urethra
- Useful for recurrent UTIs or unusual symptoms
- Can detect structural problems
Treatment Options for UTIs
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the UTI. Our urology team provides personalized treatment plans:
Prevention Strategies
Preventing UTIs is often possible with simple lifestyle changes and good hygiene practices:
💧 Hydration and Urination
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim for 6-8 glasses daily
- Urinate Frequently: Don't hold urine for long periods
- Empty Bladder Completely: Take time to fully void
- Urinate After Sex: Helps flush out bacteria
🧼 Hygiene Practices
- Wipe Front to Back: Prevents bacteria from entering urethra
- Clean Genital Area: Gentle cleaning with mild soap
- Change Underwear Daily: Keep area clean and dry
- Avoid Irritating Products: Skip harsh soaps and douches
🥗 Diet and Lifestyle
- Cranberry Products: May help prevent UTIs
- Probiotics: Support healthy bacteria balance
- Avoid Irritants: Limit caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods
- Regular Exercise: Promotes overall health
When to Seek Medical Care
While some mild UTIs may resolve on their own, certain situations require immediate medical attention:
🚨 Seek Immediate Care
- High fever (above 101°F/38.3°C)
- Severe back or side pain
- Blood in urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or mental changes
- Symptoms lasting more than 3 days
📞 Schedule Appointment
- Mild symptoms that don't improve
- Recurrent UTIs (more than 2-3 per year)
- UTI during pregnancy
- UTI with diabetes or other chronic conditions
- Unusual symptoms or concerns
Success Stories: Overcoming UTIs
Our urology team has helped many patients successfully treat and prevent UTIs:
"I suffered from recurrent UTIs for years. The team at Raksha Hospital identified the underlying cause and provided a comprehensive treatment plan. Now I'm UTI-free and feel much better!" - Mrs. Priya, 45
"The preventive strategies they taught me have been life-changing. I haven't had a UTI in over a year, and I feel more confident about my urinary health." - Ms. Anjali, 32
Get Expert UTI Care at Raksha Hospital
Don't let urinary tract infections affect your quality of life. Our experienced urology specialists provide comprehensive diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for all types of UTIs. Early treatment can prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.

Connect With Us